Self-correcting LLM-controlled Diffusion Models
CVPR 2024
TL;DR: The Self-correcting LLM-controlled Diffusion (SLD) Framework features:
- Self-correction: Enhances generative models with LLM-integrated detectors for precise text-to-image alignment.
- Unified Generation and Editing: Excels at both image generation and fine-grained editing.
- Universal Compatibility: Works with ANY image generator, like DALL-E 3, requiring no extra training or data.
Self-correcting LLM-conrolled Diffusion Models (SLD)
SLD enhances text-to-image alignment through an iterative self-correction process. It begins with LLM-driven object detection, and subsequently performs LLM-controlled analysis and training-free correction.
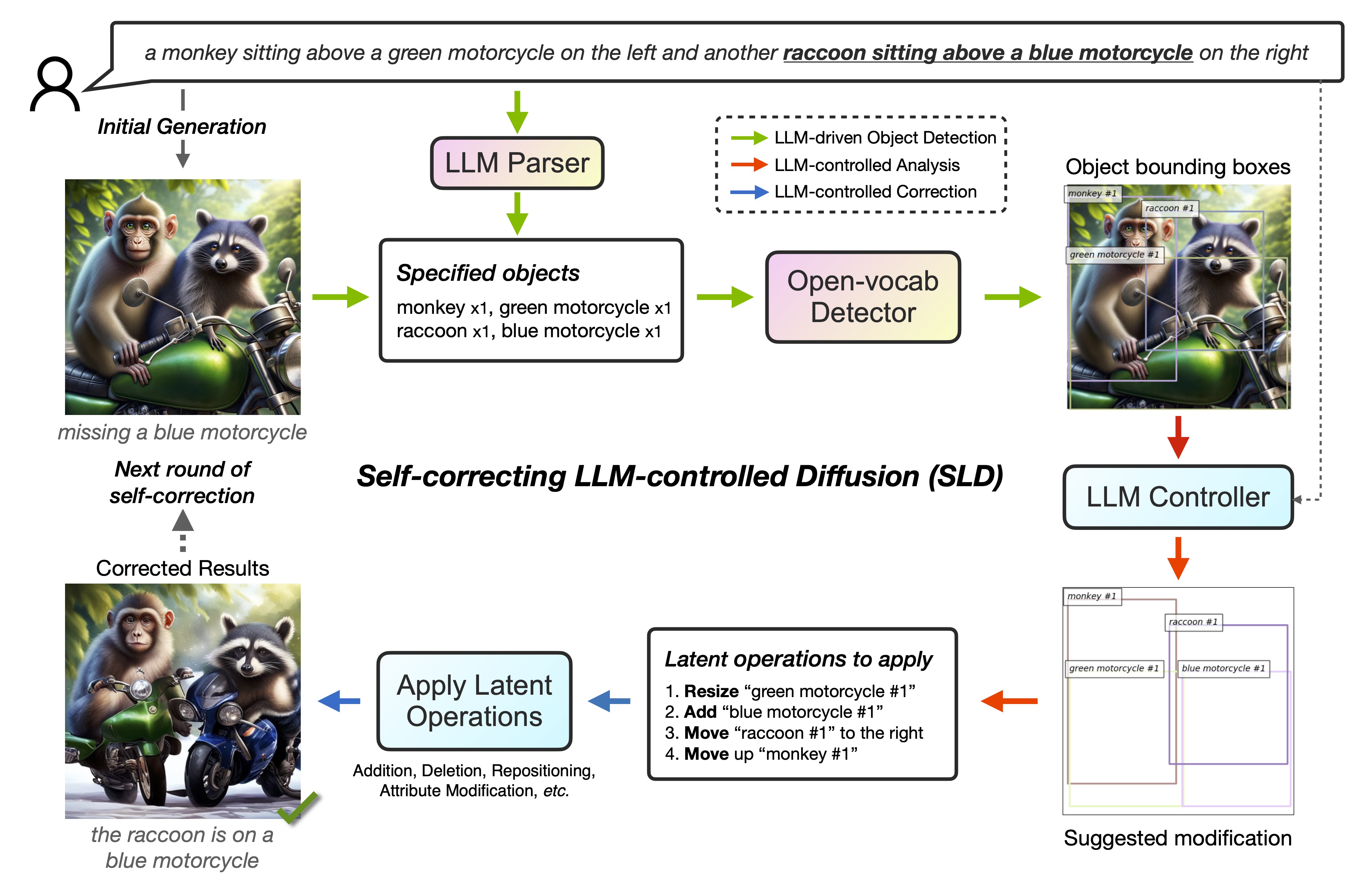
SLD Unifies Image Generation and Editing!
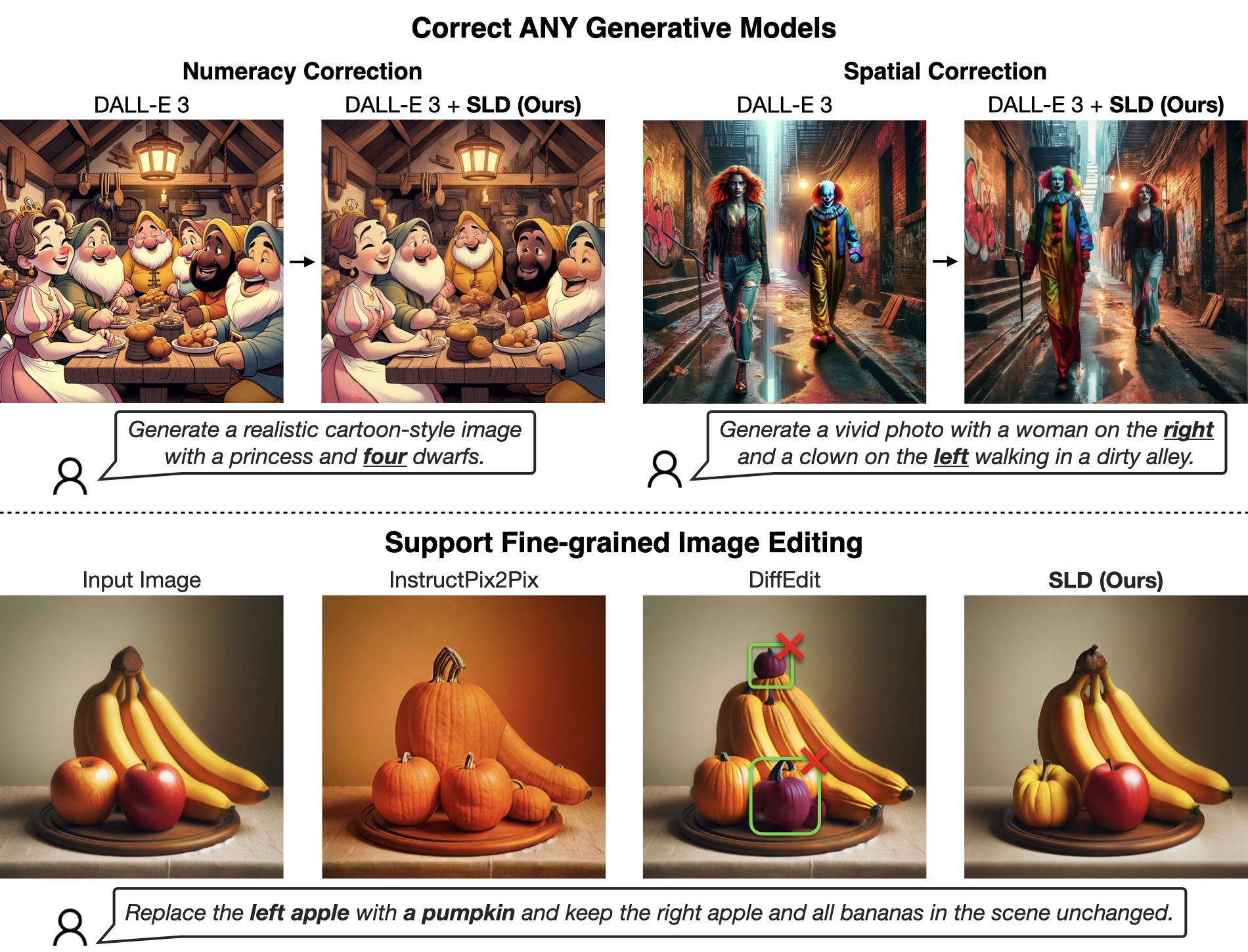
Visualizations: Correcting Various Generative Models

SLD improves text-to-image alignment in models like SDXL, LMD+, and DALL-E 3. The first row shows SLD's precision in placing a blue bicycle between a bench and palm tree, with an accurate count of palm trees and seagulls. The second row demonstrates SLD's efficacy in complex scenes, preventing object collision with training-free latent operations.
Visualizations: Complex Object-level Editing

SLD can handle a diverse array of image editing tasks guided by natural, human-like instructions. Its capabilities span from adjusting object counts to altering object attributes, positions, and sizes.
Citation
If you use this work or find it helpful, please consider citing:
@InProceedings{Wu_2024_CVPR,
author = {Wu, Tsung-Han and Lian, Long and Gonzalez, Joseph E. and Li, Boyi and Darrell, Trevor},
title = {Self-correcting LLM-controlled Diffusion Models},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2024},
pages = {6327-6336}
}
@article{
lian2024llmgrounded,
title={{LLM}-grounded Diffusion: Enhancing Prompt Understanding of Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Large Language Models},
author={Long Lian and Boyi Li and Adam Yala and Trevor Darrell},
journal={Transactions on Machine Learning Research},
issn={2835-8856},
year={2024},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=hFALpTb4fR},
note={Featured Certification}
}